Think about ordering drone supply in your takeout, after which, after consuming your meals, you eat the supply drone for dessert. The primary half has been occurring for some time; the second – the edible robotic – may very well be coming quickly, in response to scientists from the Swiss Federal Institute of Know-how (EPFL).
“Bringing robots and meals collectively is an enchanting problem,” stated Dario Floreano, director of the EPFL’s Laboratory of Clever Methods (LIS) and the lead creator of a lately revealed perspective article that thought of how far we’re from the truth of edible robots. “We’re nonetheless determining which edible supplies work equally to non-edible ones.”
At first look, meals and robots look like at reverse ends of the scientific spectrum. However, in response to the article’s authors, edible robots are usually not only a novelty you’d pay a ridiculous sum of money to see on a plate at a high-end restaurant. They’ve a variety of potential purposes in areas like human well being and vitamin, wildlife preservation and animal welfare, and the atmosphere.
There’s a lot potential in edible robots that, in 2021, Floreano joined with Remko Growth from Wageningen College in The Netherlands, Jonathan Rossiter from the College of Bristol, UK, and Mario Caironi from the Italian Institute of Know-how (IIT) to launch the RoboFood mission, receiving backing within the type of EU funding to the tune of €3.5 million (US$3.75 million) over 4 years.
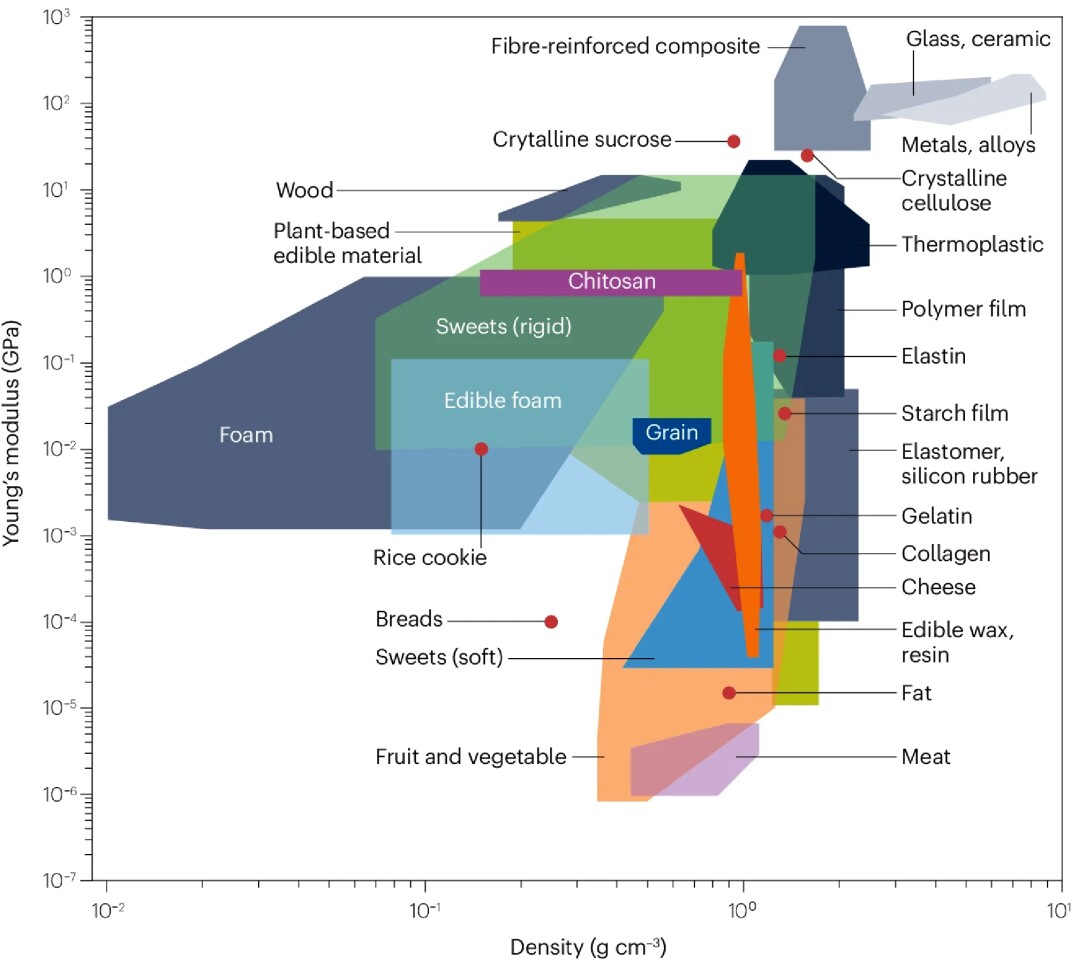
Floreano et al.
Based on the RoboFood web site, the mission’s “overarching goal” is “to put the scientific and technological foundations for the event of really edible robots and robotic meals. To that finish, let’s take a look at the event timeline for edible robots, which, like most tech-related issues, is advancing at a speedy tempo.
In 2017, EPFL scientists created a gripper able to dealing with an apple constructed from two absolutely edible actuators. The actuators had been themselves product of gelatin-glycerol materials with mechanical traits like these present in silicone elastomers.
EPFL and Wageningen scientists designed a fixed-wing drone with wings constructed from puffed rice muffins glued along with gelatin in 2022. Granted, solely the drone’s wings had been edible, but it surely flew at a pace of 33 ft (10 m) per second and will carry 50% of its personal mass as an edible payload.
In 2023, IIT researchers created an edible rechargeable battery by making an anode out of riboflavin (vitamin B2) and a cathode from quercetin, a health-promoting pure pigment present in pink onions, capers and kale. Activated charcoal elevated conductivity, whereas nori seaweed – the stuff that’s normally wrapped round your sushi rolls – was used to stop brief circuits. Packaged with beeswax, the battery operated at 0.65 volts, nonetheless a protected voltage for ingestion; two linked in a collection powered an LED for about 10 minutes.
In 2024, scientists from the College of Briston, IIT, and EPFL created the primary edible pressure sensor primarily based on digital conduction. The hot button is a novel conductive ink, a mix of activated carbon, Haribo gummy bears, and a water-ethanol combine. When the ink is sprayed on an edible substrate, each may be eaten.
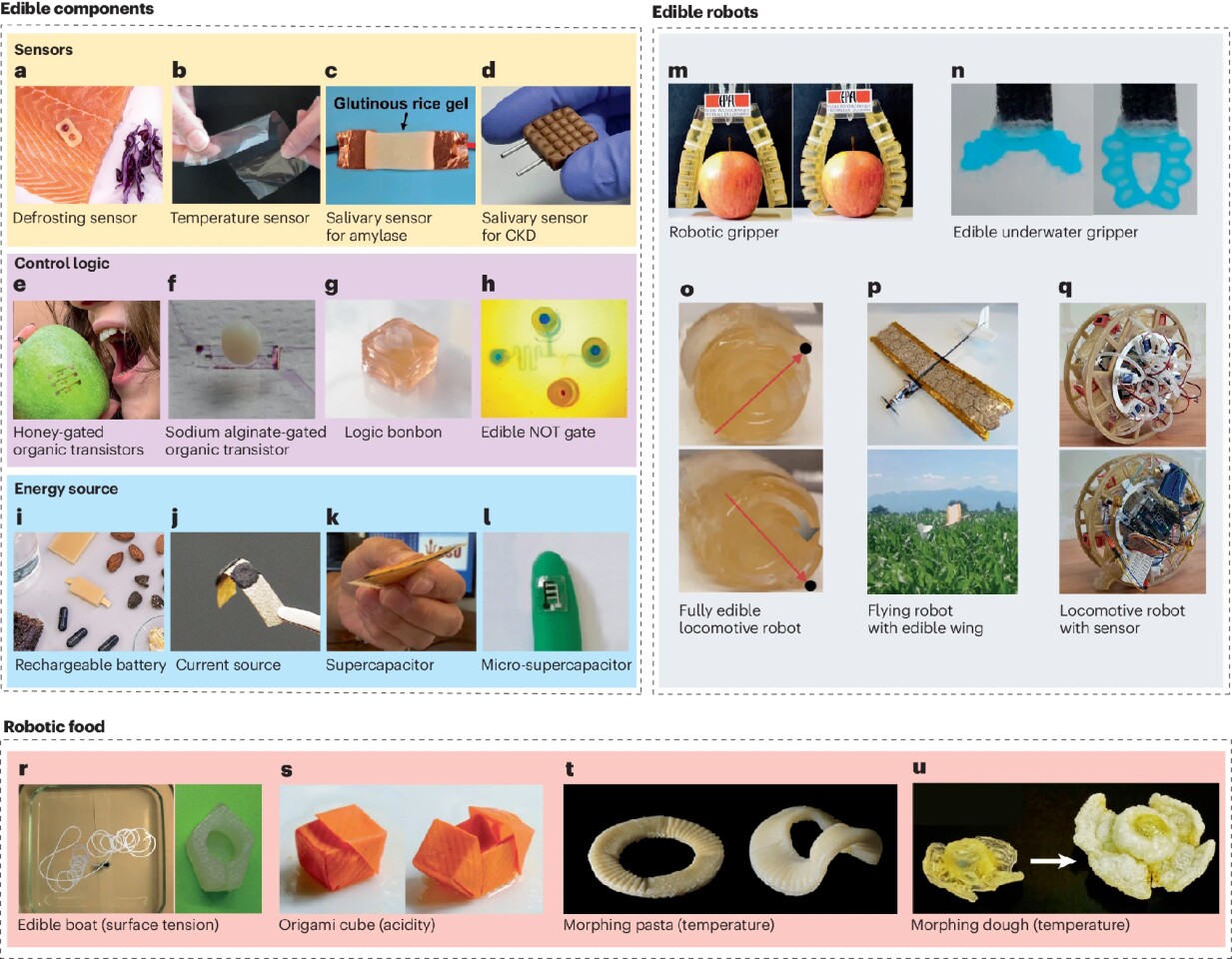
Floreano et al.
“There’s lots of analysis on single edible elements like actuators, sensors, and batteries,” stated Bokeon Kwak, a RoboFood crew member and one of many perspective paper’s co-authors. “However the largest technical problem is placing collectively the components that use electrical energy to operate, like batteries and sensors, with those who use fluids and strain to maneuver, like actuators.”
Of their paper, the researchers lay out the challenges at the moment going through the belief of edible robots. Present edible actuators and batteries nonetheless have decrease energy, endurance, and reliability in comparison with their non-edible counterparts, or they require the usage of non-edible components. One other problem is that though many edible elements are constructed from issues we usually eat, additional research are wanted to see how they work together with the digestive system. After which there’s miniaturization, making the robots sufficiently small to be a single, swallowable entity. Lastly, edible robots finally should serve some function.
So, what functions do the researchers foresee them performing? The examples they offer of their paper embody analyzing the digestive tract and exactly delivering medication, maneuvering down the esophagus to take away meals blockages, offering vitamin to people and animals, preserving the well being of untamed and domesticated animals – together with administering vaccines, environmental monitoring, and, after all, offering a novel culinary expertise. As a result of edible robots would even be biodegradable, they’re greener than the choice.
An necessary query requires a solution: How will individuals react to consuming a robotic? Some solutions had been supplied by a 2024 research the place researchers gave contributors robots constructed from sugar and gelatin – one shifting, one not – and gauged their notion and style expertise. They discovered that the shifting robotic was perceived as a ‘creature’, whereas the stationary one was ‘meals.’ Nevertheless, motion imparted better style.
The shifting robotic was often described as ‘candy,’ and contributors talked about particular tastes, reminiscent of ‘apple,’ in comparison with the non-moving robotic, which was referred to by its constituent elements, suggesting contributors believed the shifting and non-moving robots had been made of various supplies. As well as, when chewing on a shifting robotic, contributors described noticeably completely different textures to when the robotic wasn’t shifting. One attainable clarification supplied by the researchers is that contributors attributed lifelike qualities to the robotic when it was shifting; it was extra ‘alive.’
The authors of the present paper have not speculated about once we may see edible robots on our plates. Whereas the aforementioned technical hurdles nonetheless have to be overcome, we most likely will not have to attend lengthy, given the break-neck pace with which know-how is advancing.
The article was revealed within the journal Nature Critiques Supplies.
Supply: EPFL









